Throat Cancer facts
OVERVIEW
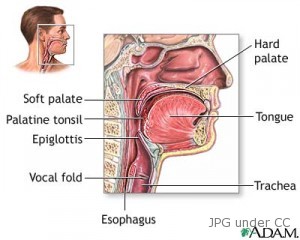
Throat cancer is generally known for cancers of the pharynx (the area connecting the mouth and the nasal cavity), vocal cords (glottis), and the larynx (voice box). It usually develops in the middle portion of the throat, which is found behind the tongue. Cancerous tumors below the glottis spread rapidly than the tumors found anywhere else.
This life-threatening disease may develop in men and women who are chain smokers, with disease in chronic acid reflux, and those with a family history of throat cancer. And according to medical research and statistics, this disease more likely develop in people whose age is 50 and above.
TYPES AND FORMS
Throat cancer is determined through their cell structure; hence, it comes in various forms such as:
- Adenocarcinoma – It is a type of throat cancer that originates in the glandular tissue. This disease is usually linked to vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and stomach cancer.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma. This disease originates in the surface layers of the body tissues. A 90% of all throat cancers comprised of this type.
- Thyroid Cancer. It is a type of cancer in the neck that affects the thyroid, a gland that regulates the body’s metabolism.
- Mouth Cancer. This disease is also termed as oral cancer, or simply a cancer that occurs in the lip or the mouth.
- Lymph Node Cancer. This type of throat cancer is commonly known as the lymphoma, which affects the lymphatic system, a system of the body that helps in fighting infection.
SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of throat cancer can be confusing as they seem to be generally associated with other health conditions.
- Chronic pain in the ears
- Chronic sore throat that does not resolve in one to two weeks even with antibiotics
- Pain or difficulty in swallowing
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Numbness in the face
- Hoarse Voice that does not resolve in one to two weeks
- Pain or difficulty in speaking
- Weight loss for unknown reason
- A lump in the back of the throat, mouth, or neck
- Breathing difficulty
- Bleeding from the blood-tinged sputum or throat
RISK FACTORS
Throat cancer is said to be the result of damage to the DNA cells of the mouth and throat. The prime cause of this damage is the use of tobacco and excessive alcohol intake. Also, people who had been infected with HPV are 32 times prone to this disease than those who are clear from the said virus.
TREATMENT
Surgery. This is a cancer treatment used depending on the throat cancer’s size and area. An endoscope (tube) is used in removing small tumors that are early detected. A part or full of the voice box is required to be removed when tumors are already medium to large size. After the total laryngectomy or removal of the entire voice box, a windpipe is connected to the neck to act as a hole through which a cancer patient breathes.
Laser Microsurgery. Patients who are suffering from cancers of the larynx, pharynx, and oral cavity often undergo the transoral laser microsurgery. It is a type of procedure used to treat small and medium tumors, but can also be used to treat large tumors. This type of treatment offers several advantages than conventional surgical procedures.
- Preservation of normal tissue
- Short duration of hospitalization
- Less impaired speech and swallowing
- May not need to undergo a tracheotomy or the insertion of a tube into the throat
Reconstructive Surgery. This is a surgical procedure performed by otolaryngologists with the aim of improving the appearance of a cancer patient, and restores the functionality of the throat as normal as possible. In addition to that, a doctor may also perform a tracheostomy, creating a hole in the neck or gastrostomy, a hole in the abdomen when the patient has a difficulty of breathing or swallowing.
Radiation. This is the main treatment performed in treating small cancer or when the patient has a poor general health and cannot undergo surgery. This treatment can also be used to kill small cancer deposits after the surgery. It can be given as a combination to chemotherapy. This provides ease from advanced cancer symptoms, such as difficulty of swallowing, pain and bleeding.
Chemotherapy. This is a type of cancer treatment that can be combined with radiation therapy. It is mainly used to control advanced stage of throat cancer that cannot be operated or has spread to other body parts. It is administered either through the mouth or into a vein.
Rehabilitative Services. This type of treatment helps patients overcome the difficulty in speech and swallowing. Dietitians are in-charge in the choice of foods that will help reduce problems associated with swallowing and chewing.
Physical and occupational therapists, on the other hand, are in-charge in helping cancer patients in making the needed adjustments for returning to work or normal activities.
