Eye Cancer facts
OVERVIEW
Eye cancer is any cancerous growth or tumor in the eye. Some eye cancers can be primary (cancer starts within the eye) and others metastatic cancer (cancer that spread to the eye coming from another affected organ of the body). Breast cancer and lung cancer are the two most common cancers that spread to the eye.
While the skin, prostate, thyroid, kidney, colon lymphoma and leukemia are the less common cancers that spread to the eye. Eye cancer is rare compared to the other types of cancer.
TYPES AND FORMS
Eye cancers are divided into 3 classifications according to the tumor’s location in the eye. These are the tumor of the eyelids and conjunctiva, orbital tumors and intraocular tumors. There are tumors that are benign, meaning they are not cancerous, and tumors that are malignant. The most common eyelid tumor is basal cell carcinoma which grows around the eye. This tumor seldom spreads to other parts.
The most common eye cancer among children is the retinoblastoma. On the other hand, intraocular melanoma is the most common eye cancer in adults. The former is a tiny tumor in the retina that keeps growing and if not treated immediately may cause further complications. The latter occurs in adults when cancer cells are formed in the uvea of the eye.
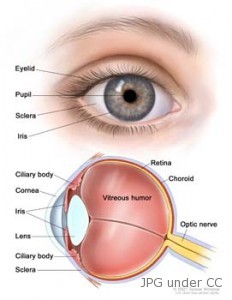
The uvea refers to the iris which is the colored portion of the eye, the choroids and the ciliary body which is an eye muscle. This type of cancer grows gradually and does not commonly spread to other parts of the body. However, if not detected or treated promptly, it may spread to the surrounding areas of the eye
The most common orbital cancer is orbital lymphoma. This is diagnosed through biopsy. Chemotherapy or radiation therapy or combination of both is the recommended treatments for this type of cancer.
SYMPTOMS
The early symptoms of conjunctival melanoma are blurring vision and tenderness of the eye. Among the later symptoms is loss of vision. An eye specialist must be consulted immediately when this happens. In the early stages of melanoma, there may be no symptoms. Only upon check up or routine tests made by a doctor can this disease be detected early.
However, as the tumor develops, the symptoms that appear are decreased vision, double or blurred vision and eventual loss of eyesight. Continuous growth of this tumor can affect the retina and cause retinal detachment.
Nevus is benign freckle in the eye. This condition should be checked regularly to make sure it does not develop into melanoma. Any dark spots that grow on the iris and conjunctiva should also be examined promptly. The symptoms of Retinoblastoma, or RB for short, are cross-eyes, reddish and painful eyes, yellowish or whitish glow through the eye’s pupil, decrease or loss of vision. RB is common in babies and young children and may occur in only one or in both eyes.
One symptom of this disease may be observed through the photos of a child. Normal eyes produces red eye reflex. However, if the child’s eye reflex is either color yellow or white, it may have a tumor or some other eye disease.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS
Genetics is known to be the cause of eye cancer. In RB, if a tumor developed only in both eyes, it is believed to be hereditary. However, if the growth developed only in one eye, heredity is not the cause. Hereditary RB has a risk of developing into brain tumor hence, constant monitoring is required.
Age and generic inheritance are factors causing interocular melanoma as well. Conjunctival melanoma is seen most often in white people. Blurred vision and tenderness of the eye are its early signs.
TREATMENT
Treatment of eye cancer depends on the condition or stage of the tumor. If the tumor is already in the advance stage, the hope of either to cure the condition or regain the vision is minimal or even next to impossible. In this situation, the recommended treatment is enucleation or eye removal. This is definitely a drastic measure and only taken as a last resort.
Surgeries may also be a form of treatment for this disease. Evisceration is the surgical procedure of removing the eye contents, leaving only the sclera (white part of the eye). With exenteration, the eye, together with the orbital contents is removed. This may include the eyelids as well.
Prosthesis could be done to improve the physical appearance. The other surgical treatments for eye cancer are choroidectomy, iridectomy, iridocyclectomy, irido trabeculectomy. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also other forms of eye cancer cure.
