Oral (Mouth) Cancer facts
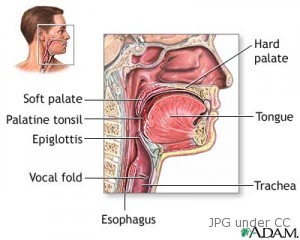
Oral Cancer Overview
Oral cancer (mouth cancer) is defined as the growth of cancer cells and tissues in the mouth. This type of cancer arises on regions such as the floor of the mouth, palate, tongue, lips, and the throat. It is believed that an approximate figure of two thirds of this type of cancer is found and present in the mouth while one third is known to emerge in the pharynx region.
Not all people know that this kind of cancer is grave and a threat to ones life. This disease kills one patient every hour that it becomes one of the most common deadly cancers among men and women in the world. Cancer cells spread relatively quickly making it even more fatal.
According to research done by the American Cancer Society, it shows that a great number of men age 50 and above are those considered of higher risk than that of women. This kind of cancer may manifest as a lesion while others are due to anatomic structure like sinuses and nasal problems.
TYPES AND FORMS
Oral cancer is categorized into two forms. First, based on the location of cancer, and secondly, the origin.
The site/location of the cancer
Oral Cavity Cancer – This form of cancer starts in the mouth area, the lip, floor of the mouth, hard palate, jaw, cheeks, salivary glands, teeth and tongue.
Oropharyngeal Cancer – This type of cancer starts from the pharynx and other neighboring regions such as the soft palate, the tonsils, uvula and base of the tongue.
The origin of the cells
Squamous Cell Carcinoma – This type of cancer is either positioned in the lining of the cells known as carcinoma in situ and the one outside the layer called squamous cell carcinoma. This is the most common cancer of the mouth where a figure of 90 percent is recorded. This is also said to be apparent among those who are frequent tobacco chewers.
Minor Salivary Gland Cancer – This is a type of cancer known to originate in the salivary gland.
SYMPTOMS
Oral cancer is a kind of disease that needs careful attention. A regular visit to your dentist or a doctor will help you see the early warning signs of a possible oral problem. Therefore, checking the tissues in your mouth as a part of your oral check up is a must. Check out these following symptoms:
- The presence of white patches (leukoplakia) and red patches (erythroleukoplakia) in the mouth. White patches are known to be a malignant type of cancer while red ones are not.
- The occurrence of lumps and sores in the mouth, throat and lip area.
- A seeming complicated movement of ones jaw.
- Difficulty in swallowing and chewing foods even with small portions.
- The inability to put dentures in the right and comfortable way.
- The tongue and other parts of the mouth become insensitive and numb.
- A loose teeth
- The feeling of a lump in the neck and jaw area.
CAUSES
In the United States in 2008, 34 thousand are found to be suffering with mouth cancer. Most of these are diagnosed when already at the late stage of the disease. The incidence of oral cancers are more commonly found in men than women because they are the ones who use tobacco and alcohol, which are considered to be the main cause, over longer periods of time and in larger doses. It most commonly starts after the age of 35, wherein half of all diagnosis are from the 68 years and older.
Although the exact cause is unknown, it is tobacco and alcohol that is considered to be the number one causes of mouth cancer. Some forms of the virus are also considered a cause for this cancer, e.g., version 16 of the Human Papilloma virus. It in fact attributes to 20 to 30 percent of oral cancer cases. Another cause is the long exposure to the sun, particularly for lip cancer. Unhealthy diet, especially one which is lacking in fruits and vegetables may also be a cause.
There is no exact cause of this kind of cancer in the mouth but there are certain factors that may increase the risk of having health issues orally.
- Cigarette smoking – This tops the possible root causes of oral disease specifically those who smoke smokeless tobacco.
- Too much exposure to UV rays – Lip cancer is the most common of all these types of root causes. Too much exposure to the sun without protection will result to cancer growth.
- Excessive alcohol consumption – Based on conducted studies in the recent years, too much drinking of alcohol coupled with smoking results to 80 percent greater risk as cancer cells tend to act synergistically.
- Ill fitting dentures – This normally causes lumps and oral infections in the mouth.
- Poor oral hygiene and deficient diet – Lack of important vitamins and minerals such as vitamins C, E and iron are considered big factors. Needless to say, poor hygiene when it comes to properly cleaning the mouth is another significant aspect to look at.
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
The best thing that could be done to prevent mouth cancer is to decrease, or better yet stop the use of tobacco and alcohol. Thought there was an increase of its use in the 1990s, recent statistics shows that this has leveled off and is beginning to decline. If this continues, there will be a lower chance of getting oral cancer in the next generations to come. Mouth cancer could also be prevented by not exposing yourself to sunlight over long periods of time.
With regards to treatment, it is commonly recommended, for small-sized tumors, to have it surgically removed or excised. For tumors that are deemed inoperable, radiation therapy is the more radical alternative. For larger sized cancers, although surgery may also be the answer, it is nonetheless taxing and technically demanding due to the delicate nature of the head and neck areas. Reconstructive surgery, skin graft and bone graft may sometimes be required to restore the facial form close to normal. Another form of treatment is chemotherapy which may be combined also with radiation therapy since it seldom used alone in treating cancers. For cases wherein cure is already impossible, chemotherapy can considerably prolong the life of the cancer victim.
Surgical procedures allow for the removal of the tumor and other fatal lumps that may lead to further infections and recurrence rate of oral diseases. Among the surgical procedures that can be done to treat this kind of cancer are as follows:
- Primary tumor resection – This is where the removal of the tumor and infected tissues are done.
- Mohs’ micrographic surgery – This is the latest technology of all types of surgery. This allows the removal of entire cancer cells from the roots. This is particularly done when the growth or lump is in the lip area.
- Mandible resection – This is a surgical procedure where the removal of tumor coupled with the jaw bone is performed.
- Maxillectomy – When cancer cells have already spread, the removal of the tumor and the hard palate is done.
- Laryngectomy – Those who have large tumors undergo in this type of surgery. In most cases, the voice box of a person is completely removed.
