Colon & Rectal Cancer facts
Colon Cancer Overview
The colon is the part of the digestive tract where the waste products are stored. The rectum (the end of the colon) together with the colon, form the large intestine (also called as the large bowel).
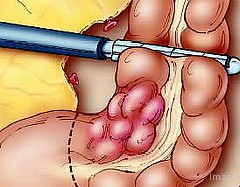
Tumors of the colon and rectum are found on the inner wall of the large bowel. They may have 2 types: benign and malignant tumors. Benign tumors which are also known as polyps do not spread to other organs and are not so dangerous. But if not timely removed, they can change into cancerous tumors in a short time.
Malignant growth that is cancer of the colon and rectum can damage nearby tissues and organs, as well as distant parts of the body. Such spread of colon cancer to distant organs is called metastasis of the colon cancer.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
Colorectal Cancer may have a wide range of symptoms. The primary symptoms that a patient may experience include:
- Weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Irritable bowel syndrome symptoms such as irregular bowel movements, diarrhea or constipation, cramps or bloating, abdominal pain, narrow stools, etc.
- Red or dark blood in stool
- Ulcerative colitis, Peptic ulcer, Crohn’s disease, Diverticulosis, etc.
Unfortunately, sometimes, symptoms can become obvious after several years of existing of the disease and may vary depending on which area of the large bowel the tumor is located in. If cancerous tumor appears in the right (ascending) colon, it can grow to larger sizes before this leads to any abdominal symptoms, as this part of the colon is spacious. The most common symptom of right-sided colon cancer is anemia that in turn, causes weakness, fatigue and shortness of breath.
Cancers of the left (descending) colon may cause partial or complete bowel obstruction due to its narrow size. This can be accompanied with constipation, narrowed stool or diarrhea, abdominal pains and spasms, bloating, etc.
CAUSES & RISK FACTORS
The following factors can lead to colon cancer:
- Diet. Colon cancer may originate from a low fiber, but high fat diet. Especially, people who prefer red and processed meats are at a higher risk.
- Hereditary – You are at a high risk of colon cancer, if one or more members in your family have this disease.
- Age – Colon cancer occurs mostly in those people who are over 50.
- Smoking and Alcohol – People who abuse alcohol or cigarettes are at greater risk of colorectal cancer.
A numerous diseases or disorders, including inflammatory intestinal conditions, growth hormone disorder, diabetes, obesity, etc. can also lead to colon cancer.
PREVENTION
The most effective prevention of colorectal cancer is early determination and removal of benign colon polyps before they turn into malignant tumors.
TYPES & FORMS
Adenocarcinomas: Adenocarcinomas (found in 90-95% of colorectal cancer cases) have 2 forms: mucinous and signet ring cell.
Leiomyosarcomas : This type affects the smooth muscle of the colon. Leiomyosarcomas account for less than 2% and have a high risk of metastasizing.
Lymphomas : Colorectal lymphomas are rare (about 0.5%) and usually occur in the rectum, though it can affect the colon too.
Melanomas : This type of colorectal cancer is also very rare and usually originates from a melanoma started in another part of the body, and then spreads to the colon.
Neuroendocrine Tumors : This type of tumors has two main forms: aggressive and indolent. Large cell and small cell neuroendocrine tumors are considered to be aggressive, when carcinoid growth is considered indolent.
Diagnosis
Though there are many ways to diagnose colon cancer, they are all similar in one thing: laboratory analysis of a tissue sample to confirm the existence of the disease.
A patient can take one or several of these five tests: virtual colonoscopy, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, barium enema and fecal occult blood test.
One of the main options in diagnosis of colon cancer is a biopsy. This is the removal and examination of tissue sample from your colon that is finally analyzed in a laboratory to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Colon Cancer Facts
- It’s estimated that 90 million Americans are at risk for colorectal cancer.
- Cancer of the colon and rectum is the 3rd leading type of cancer in males, and the 4th in females in the US
- Unlike Asia and Africa, it is mostly found in the countries where western diet is popular (US and Europe).
- Surgery is the most common treatment for colon & rectal cancer.