Skin Cancer facts
What is Skin Cancer?
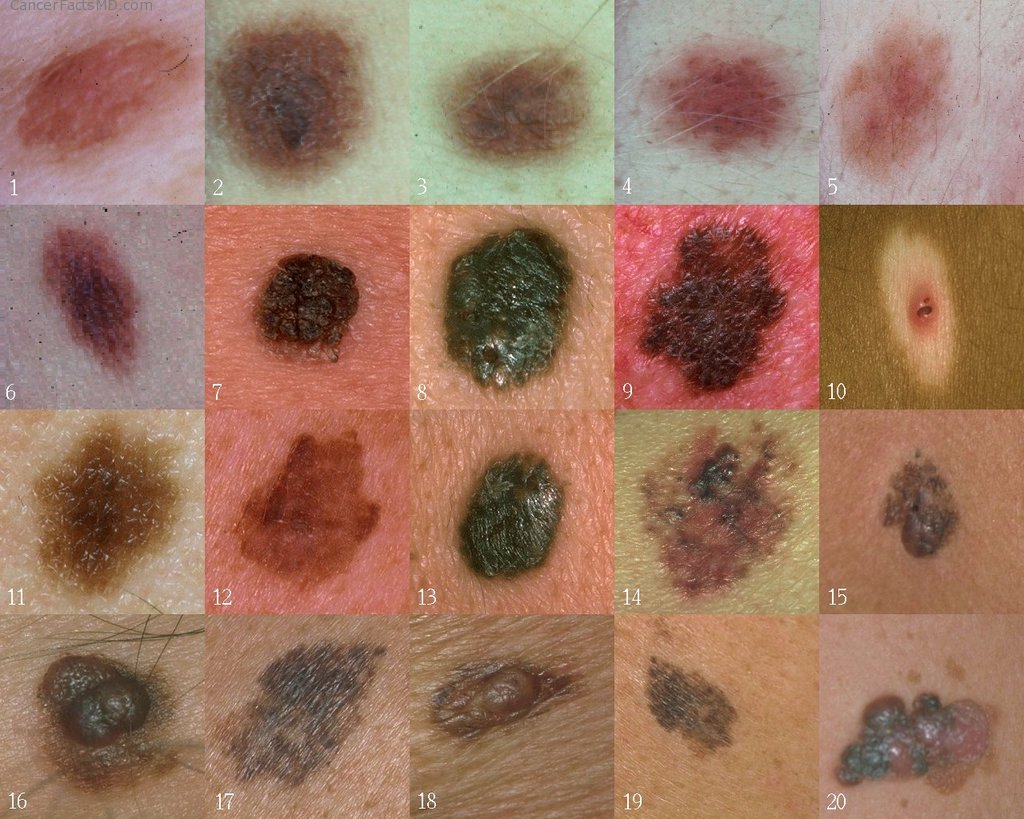
Skin cancer is a result of the abnormal and uncontrolled division of skin cells. The types of skin cancer that can occur include basal cell, squamous cell or melanoma. Basal cells carcinoma and squamous cells carcinoma are easier to cure then melanoma, which has the highest mortality rate. With as many as 500, 000 new cases occurring annually, this disease is the largest single source of malignancy in the US. An estimated 6,000 persons die of this disease every year.
TYPES AND FORMS
There are four primary types of skin cancer which include:
- 1. Actinic Keratoses (Solar keratoses) is the precancerous stage in the development of skin cancer whereby early detection of this stage has been proven to be curative for most of the skin cancers.
Most of the time, it manifests itself as small, scaly and itchy spots commonly found on the face, neck, lower arms and on those areas of the body which are exposed directly to the sun rays without proper use of protection such as sunscreen application or wearing a long-sleeved shirt and long pants will provide optimum protection. As suggested by its name, solar keratoses simply mean prolonged direct exposure to UV sun lights.
- 2. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is the most common of all skin cancer which likely to grow relatively slowly on particular parts of the body such as skull, face (central area), neck and hands. Sometimes, it can even take several months or a year even to grow to a diameter of one-half inch. As a result, its initial sign could be a spot or lump which is never healed and the diameter can be enlarged over the next 5 years and so on.
- 3. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common type of cancer after BCC. It usually occurs locally on the fairer skin compare to the darker tones with a faster growing rate than BCC. It can grow into large masses and can even become invasive metastases to other parts of the body. It is also 3 times more likely to be found in men than women.
- 4. Malignant Melanoma is the most dangerous type among all the skin cancer. However, it can be prevented and cured if it was detected early. It involves the melanocytes skin cells which produces melanin (a dark brown pigment) concentrated within the epidermis.
Initially, it manifested as a melanoma lesion and can be located anywhere on the body (palms, soles, under the nails, in the mouth), but it is most common on the lower extremities in women and back and trunk in men. It usually appears suddenly or begins in or near a mole. In some cases, melanoma may not only affect the skin, but can also metastases through the blood or lymph system.
People of all ages are in risk yet it commonly afflicts the young and middle aged. Melanoma strikes more to white populations than the blacks and the Asians. Research says that melanoma in blacks is 1/20 than that of whites.
ETIOLOGY (CAUSES)
As in other malignancies, the etiology and causes of this disease is not fully understood. However, it is believed that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a critical factor in the incidence of skin cancer. Hence, anyone could be at a risk of skin cancer regardless to the types of skin color.
However, this disease is mostly associated with the latitude and the intensity of radiation exposure. Hence, people who have fair skin, light-colored eyes (blue and green), blonde or red hair, high degrees of freckles, tendency to sunburn and rarely tan with exposure to sunlight are especially at risk.
Owing to this, this disease is most common in United States than any other countries of the world and it has surpassed heart disease as the number one killer disease with more than 1 million non melanoma skin cancers are diagnosed each year, and approximately one person dies from melanoma every hour.
SYMPTOMS
In general, the sign and symptoms of this disease are:
- Abnormal appearance or changes in size, color, shape or elevation of a mole.
- Unhealed or thickened (pigmented) red patch or spots that may be itchy. It is mostly found on women’s legs or even on the moist membranes, for example in the mouth.
- Presence of small blood vessels growing near the tumor.
The symptoms of non-melanoma skin cancer may be similar to symptoms of other non-cancerous skin conditions. Hence, it is recommended to check with your GP and notify him of the prevalence of these symptoms.
PREVENTION
Since UV radiation is one of the major causes, protection from harmful sunlight is of paramount importance in decreasing the risk of skin cancer. The most hazardous radiation from sunlight is between 10 am and 4 pm, hence it is suggested to stay out of the sun at these hours or by avoiding direct exposure to the sunlight through the application of sunscreen (particularly in blocking towards UVA and UVB broad spectrum radiation).
Wearing protective clothing such as long sleeves, wide-brimmed hat and gloves can also help in reducing direct sunlight exposure.
Periodic self-examination of skin characteristic may also aid in early detection of this type of cancer especially actinic keratoses which has high curing rates. This can be performed through the use of a full-length mirror and a handheld mirror to check the entire body for any abnormal moles or other lesions.
As a step toward self-prevention, you must be alert of the symptoms of skin cancer. If there is any doubt, you must contact your GP for further diagnosis.